Table of Contents
Introduction
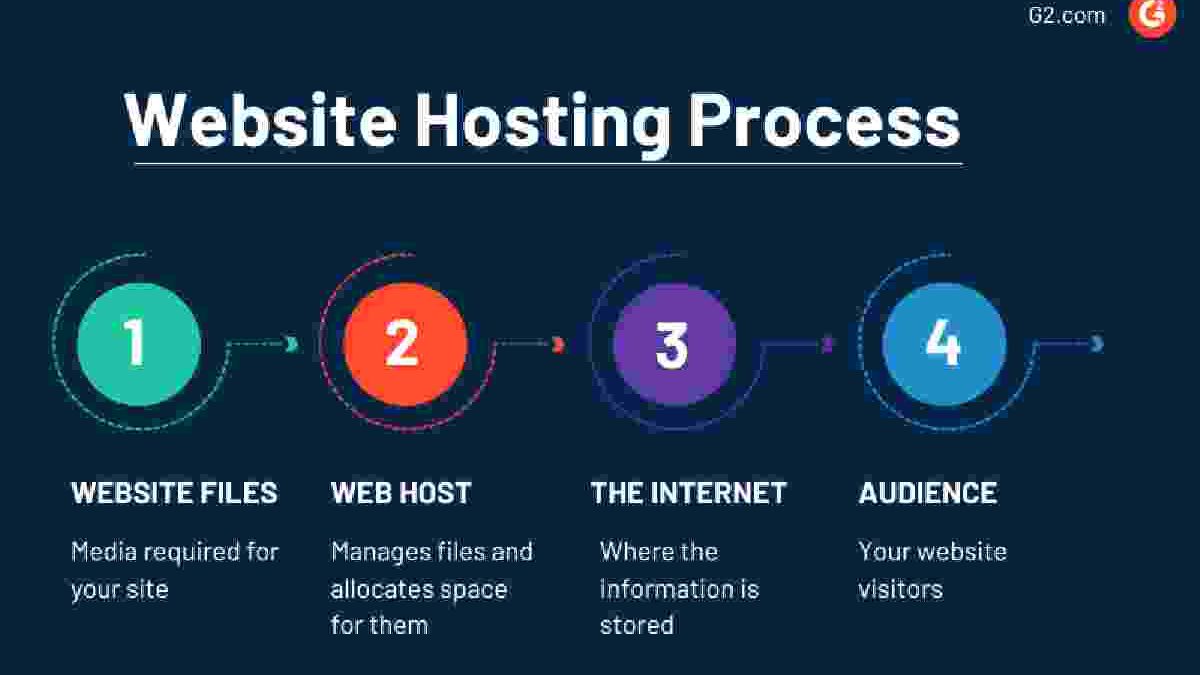
When hosting a website, you have to maintain the right balance between many variables, always affordable access to your site, and scalable, low-cost maintenance to get the perfect location; it’s like balancing on a rope.
Everything starts with where you can host your site and how.
There are generally two basic types of hosting: hosting your site yourself, called self-hosting, or using someone else or a specialized platform to host your site.
The use of self-hosting is now rare.
Why Is Self-Hosting Useless?
You can host a website from your computer. But the possibility of self-hosting does not necessarily mean that it remains chosen.
Initially, you should check that the webserver has a continuous power supply and an alternative once the power is out.
You must have sufficient expertise to install the hosting infrastructure and allow internet traffic to reach your self-hosted site through the firewall. No one else is there to set up, build and maintain the webserver.
You’ll then have trouble setting up your web host, as you won’t be able to send an email because almost all isps block outgoing traffic through port 25 to prevent spam from being sent.
In the end, self-hosting a website brings with it a lot of problems, in addition to the fact that server maintenance and monitoring are essential and must be continuous, require specialized skills. Moreover, if not well done, your site visits may stop; it is a useless way only for small business teams used internally and certainly not worth the trouble of hosting a website operated by the public.
how to host a website – low-cost scalable maintenance – self-hosting – use a platform to host your site – web hosting
Web Site Hosting Requirements:
the most straightforward way is co-hosting. Using type, other site owners remain granted access to the same physical server, i.e. they all share the same hardware resources, despite having separate accounts.
In this type, the cost of server maintenance remains divided among site owners, which is a tremendous advantage of co-hosting.
However, co-hosting provides limited resources. Therefore, to ensure that its customers have the same level of service, co-hosting providers usually have strict resource constraints, such as CPU, physical memory and bandwidth.
Another type of hosting is called dedicated server hosting. This type of hosting offers you a complete server. You won’t share the server or any of its resources with anyone, and you’ll get it in full.
Another type of hosting combines the previous two types, known as the private virtual server or VPS hosting. Thanks to virtualization, the service provider divides the large server into smaller isolated virtual servers. Each unit operates independently of the other, forming smaller dedicated hostings.
Personalized hosting is the perfect choice for large bandwidth websites and storage requirements.
Location Types Website Hosting
Generally, websites can remain divided into two main categories:
Fixed websites, the simplest, are usually manually programmed in HTML format or with the help of web design software such as Blocs, Rapidweaver and Pinegrow Web Editor before uploading them to the hosting provider’s server.
One of the advantages of this type is the ease of design and the low maintenance costs. But they offer limited job options making it more challenging to perform some everyday online tasks, mainly performing operations or interacting with visitors.
The second category is dynamic websites. This website relies on scripts to create and update content and HTML. Dynamic websites remain usually operated by content management systems (CMS) such as WordPress and Joomla.
You can interact with and influence the website using the site’s content management systems and help simplify some of the complex and basic online tasks that may have been nearly impossible with fixed websites.
Features Required Website Hosting
the next step is to purchase from the appropriate hosting provider.
There are a lot of providers, but they all differ in price and services provided. Judging the quality of the provider depends not only on the fees it offers but also on additional features because it’s more complicated than just hosting the site, i.e. making it available online, so good hosting providers add more basic services.
you can categorize suppliers accordingly to many other factors; here are some of the more essential aspects we consider:
Bandwidth:
You should slow down the amount of bandwidth for your site unless you host a personal website or an online resume; that will be rare. You can start with the lowest level of purchasing plans for hosting providers; if you plan to host a website with a lot of multimedia content, you’ll need a lot of bandwidth even at first.
Scalability:
It would help if you slowed down to think about the future of your project and the current requirements of your site. For example, your site will attract more visitors if your business is good. To serve the increasing number of visitors, you may have to look for hosts to meet your growing storage requirements – download more content – or bandwidth.
Linux Or Windows server:
Most web hosting service providers offer Linux and Windows servers. Choosing the right system for your website doesn’t depend on the operating systems you run on your desktop. Just decide to host Windows if your site requires Windows tools such as ASP.NET, MS SQL, Web Server IIS, etc. You can use Linux hosting for other website types.
Website Hosting Builder:
Web hosting providers have a range of utilities and control panels such as cPanel and Plesk to help you manage your site. A helpful tool is the web creation tool. If you plan to develop your location, look for a provider that provides an online website creation tool.